ATEC:Atomatic Tight Edges Control.
Induction roll edge heater / Hot oil sprays
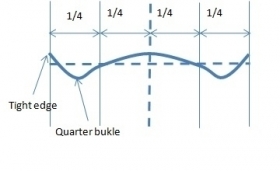
MATPROCESS offers a systems in order to manage the tight edges looking for improving quality and production rate with more percentual of reduction at each pass. The tight edges in the strip are connected with the quarter buckles, W profile, as the result of the elastic deformation of the working roll (wr) supported by the backup roll (br) under distributed load, with poor thermal gradient profile in the working rolls, and flattening. If you observe in the monitor the shape of the first part of the coil rolled after wr change , you see this W shape.
It normaly happens after work rolls are changed, in the first part of the coil, the wr have low temperature and is not possible to generate, with the spray cooling, a thermal gradient in the wr quarters or , when from one pass to another there is a big rolling load variation. In this condition, W the bending is frozen (if the bending try to remove tight edges, moving in negative direction, the quarter buckles grows) only the cooling have the chance to generate thermal gradient in the quarter. In order to generate the thermal gradient, with the spray cooling opened at the quarter of the wr to reduce the quarter bukles, it needs time and when this appen for the bending is possible to move in negative direction to reduce the tight edges. During this time we generate quarter bukles and tight edges in the rolled strip.
To fasten the flatness correction it' s possible to heat the work roll (wr) outside the strip width, where the tight edges are. There are two systems to do this, spraying hot oil or activating inductor in order to generate thermal gradient that grow the diameter of the wr , reducing the tight edges.
In this condition, without tight edges, the bending goes in positive removing the quarter buckles. All this functionality are driven by the AFC software presented above.
ABSC : Automatic Bending Support by Cooling.
MATPROCESS provides solutions in order to automatic managing the bending in the following conditions:
During cold rolling, a big change of the paschedule, width [mm] or/and load [N], generates a request of bending over the maximum +/- 100% with flatness problems (central bags, lateral waves) for the first part of the coil.The automatic flatness control (AFC) remove the flatness problem through the cooling sistem, but it has need time, the first part of the coil is without flatness, 100/500 meter of strip.
During passchedule changes, width change and load change, with this functionality ABSC, the bending is continuosly drived in a predetermined gap near +10% +15%, with the cooling management, generating a predetermined thermal crown in the working rolls, in this manner there is at disposal for the bending the +/- 90% of the full scale for overcome the big variation in width and load. This moves the limits of the paschedule assembling semplifying it and remove flatness problems in those phases.
MATPROCESS develops mathematical models for:
CMM : Cold Mill Model
- Excel file
- Data entry for fix technicals Mill data like rolls dimension , motors data, etc.
- Data entry for different alloys for define yield strength vs hardening (flow stress)
- Paschedule generation with intermediate annealing.
a-free, with introduction of the entry, exit thichness
at varius passes, width , alloy
b-costant reduction for minimize the total lenght of the
rolled material (contact time reduction),
with introducion only the N° of passes, width , alloy.
5. CMM cold mill model calculates :
a-Entry exit thickness for costant reduction [mm]
b-Entry exit tension [N] in the respect of, wr slipping,
minimum friction
c-Arc of contact [mm] , wr flattening, rolling load [N]
d-Friction μ (Avitzur)
e-Exit coil temperature [°C]
f-Productivity [Ton/h]
g-Energy consuption [kwh/ton]
PLM : Paint Line Model for 2 curing ovens description.
1-Excel file
2-Data entry for fix technicals Paint Line data like max speed [m/1'], max exaust air capacity[Nm^3/h], curing ovens lenght [m], thermal capacity[kwh/m^2], minimum oxigen level[%], LEL[%,grs/m^2], etc.
3-Data entry for different paint type, primer and finish, solvent [grs/m^2], peack metal temperature PMT [°C], etc
4-Process data entry, strip alloy, thickness [mm], width [mm] and:
a-free, with introduction of the zones curing ovens
temperature [°C], linee speed [m/1'], for research the
strip PMT [°C] and particular temperature profile in the
zones.
b-for maximize the productivity [ton/h], with introduction
the PMT [°C]. The sistem calculate the strip speed
[m/1'] for reach the PMT in the last zone with the
max temperature for each zones.
5-PLM paint line model calculates :
a-PMT[°C] , strip profile temeprature in the ovens zones
[°C].
b-Line speed [m/1'].
c-Exaust, fresh, hot air flow rate [Nm^3/h].
d-Level Explosion Limit LEL [%], Oxigen level O2 [%].
e-Thermal energy consuption [kwh/ton].
f-Productivity [Ton/h].